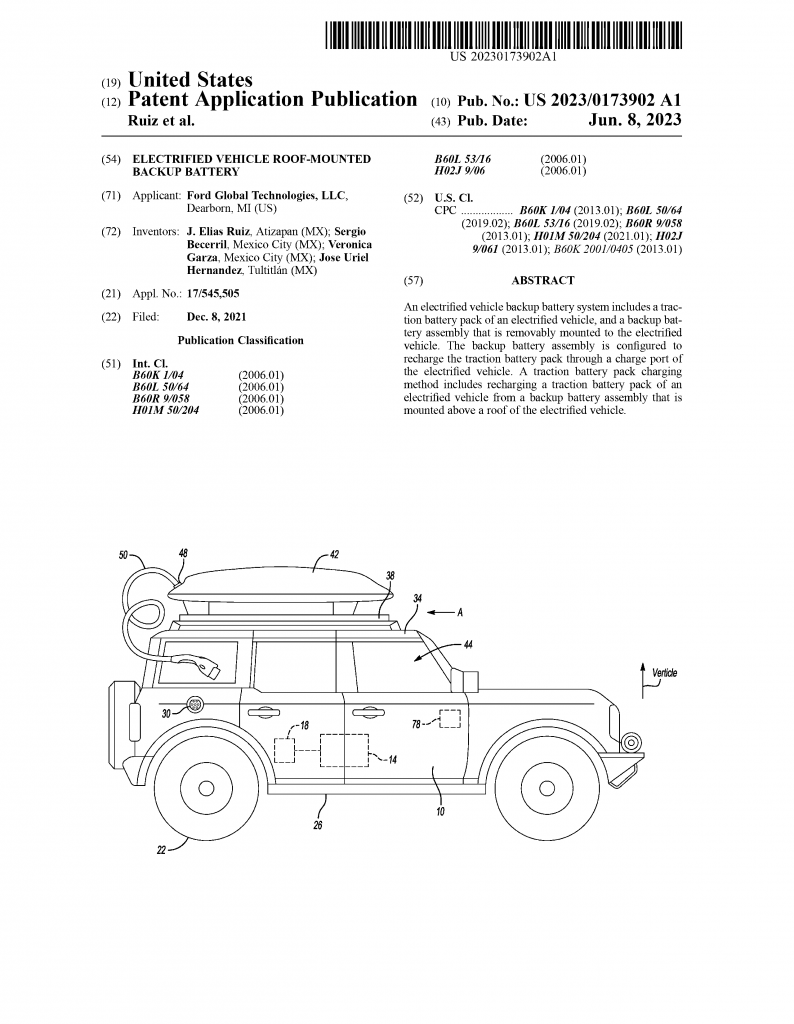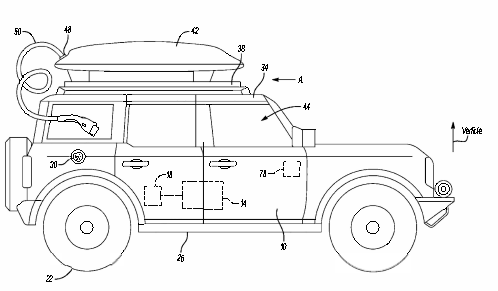
Addressing the persistent challenge of range anxiety in electric vehicles (EVs), Ford has made substantial strides by unveiling a patent application titled “Electrified Vehicle Roof-Mounted Battery Backup.” Originally filed on December 8, 2021, and published by the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) on June 8, 2023, this visionary concept introduces a groundbreaking solution to extend EV range, coupled with advanced control features.
Tackling Range Anxiety with Cutting-Edge Control
Ford’s patent application dives deeper into the solution for range anxiety, providing insights into the role of advanced control mechanisms. As a pivotal component, the backup battery assembly 42 boasts multiple battery modules and a connection port. To manage energy transfer and ensure seamless operation, a controller module has been integrated into the system. This controller module is designed to communicate wirelessly with a communication module installed in the electrified vehicle.
The wireless communication between the controller module and the communication module utilizes technologies like Bluetooth or other wireless communication protocols. This wireless connection enables precise control over the recharging of the traction battery pack using energy stored in the backup battery assembly. Essentially, the controller module plays a vital role in orchestrating energy transfer, optimizing efficiency, and enhancing user control.
Charging Method: Efficiency and Convenience
The patent application outlines a method for recharging the traction battery pack using the backup battery assembly, emphasizing efficiency and user convenience. The process entails several key steps:
This method simplifies the process for EV users, ensuring that they can take advantage of the backup battery assembly’s extended range capabilities with ease.
Adaptability and Accessibility
What sets this concept apart is its adaptability to various usage scenarios. In some instances, the removable mountable backup battery assembly is designed as an aftermarket item, allowing existing EV owners to retrofit their vehicles for extended range when needed. Alternatively, the assembly can be leased or rented before embarking on off-roading adventures or remote trips, providing a flexible solution for a wide range of EV users.
Claim 1: An Electrified Vehicle Backup Battery System
Claim 1 of Ford’s patent application outlines the core elements of this electrified vehicle backup battery system, highlighting its innovative features:
A Visionary Solution with Endless Possibilities
In conclusion, Ford’s patent application for an electrified vehicle roof-mounted battery backup represents a visionary solution to the persistent issue of range anxiety in electric vehicles. With advanced control features and a seamless charging method, this concept aims to make EVs more versatile and suitable for diverse driving scenarios.
While the concept holds great promise, it’s important to note that the preceding description is exemplary rather than limiting. The potential for variations and modifications that do not depart from the essence of this disclosure is acknowledged. As technology continues to advance, the scope of protection for this groundbreaking solution can only be defined through further exploration and study.
A technical perspective regarding the risks associated with Ford’s roof-mounted backup battery technology for electric vehicles (EVs):
Weight Distribution and Center of Gravity: Adding a substantial battery on the roof can significantly alter the vehicle’s weight distribution and center of gravity. This can lead to handling issues, particularly during cornering and sudden maneuvers. Automakers must conduct extensive simulations and testing to ensure the vehicle remains stable and compliant with safety standards.
Structural Integrity: Roof-mounted batteries introduce structural challenges. The vehicle’s roof and body must be reinforced to bear the additional weight safely. Weak points in the vehicle’s structure could compromise safety in the event of a collision. Rigorous crash testing and structural engineering are imperative to address this risk.
Aerodynamics and Efficiency: The aerodynamic profile of an EV plays a crucial role in its efficiency and range. Placing a bulky battery on the roof disrupts airflow, increasing drag and reducing efficiency. Engineers must work to minimize these effects through aerodynamic design and optimization.
Installation and Removal Challenges: Mounting and dismounting a heavy battery assembly on the roof can pose practical difficulties. Users may require special equipment, which could deter adoption. Ensuring a user-friendly and safe installation process is essential.
Electrical Compatibility: Integrating the backup battery with the vehicle’s electrical system is complex. Compatibility issues, such as voltage disparities or communication protocol conflicts, could result in malfunction or safety risks. Rigorous electrical engineering and testing are vital to mitigate these risks.
Complex Control Systems: The advanced control mechanisms mentioned in the patent require robust software and hardware. Software bugs or system failures could lead to unpredictable behavior, affecting both vehicle safety and performance. Stringent software development and testing protocols are critical.
Regulatory Compliance: Meeting safety and regulatory standards is paramount. Roof-mounted batteries must adhere to crash safety standards and electrical safety regulations. Moreover, they must comply with transportation regulations regarding vehicle dimensions and loads.
Weather Exposure: Roof-mounted batteries are exposed to the elements, including rain, snow, and extreme temperatures. Ensuring the assembly’s durability under these conditions is vital. Sealing, insulation, and thermal management systems must be meticulously designed.
Infrastructure and Charging Compatibility: The technology must seamlessly interface with various EV models and charging infrastructure. Compatibility issues could result in charging failures or damage to the vehicle. Thorough compatibility testing and standardization efforts are necessary.
User Interface and Experience: A seamless user experience is crucial for user acceptance. Users should find it intuitive to install, charge, and operate the backup battery assembly. A poorly designed user interface could lead to user errors or dissatisfaction.
Market Viability and Adoption: The success of this technology depends on market acceptance and cost-effectiveness. Consumer preferences and willingness to adopt a backup battery solution for extended range in EVs are uncertain. Market research and strategic pricing are essential.
Environmental Impact: The production and disposal of additional battery modules raise environmental concerns. Sustainable manufacturing and recycling practices should be prioritized to minimize the environmental footprint.
In summary, while the roof-mounted backup battery technology holds promise for addressing range anxiety and enhancing EV versatility, automakers face a myriad of technical challenges that demand rigorous engineering, testing, and adherence to safety and regulatory standards to ensure its viability and safety in the highly competitive EV market.
Citations: